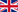
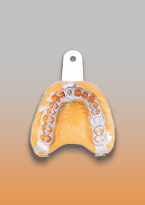
Impression materials are substances with which impressions are obtained from the teeth and jaws for further prosthetics. All of them are divided into three groups: solid, thermoplastic and elastic. Solid ones (gypsum, zinc-eugenol pastes) harden in the oral cavity, give accurate casts, adhere well to the impression tray, but are more difficult to remove from the oral cavity than plastic ones. Thermoplastic materials change consistency depending on body temperature. Compared to solid ones, they are more convenient to work with, but casts from them are less accurate. Elastic impression materials acquire a rubber-like state when solidified. Impressions with their help are obtained as clear as possible, and the procedure for removing such an impression is easily tolerated by the patient.
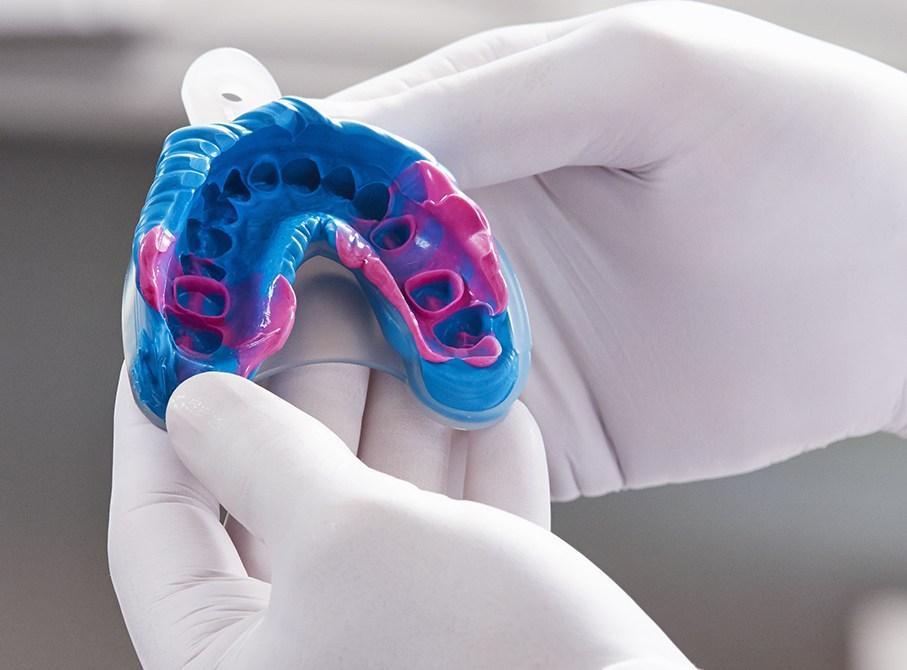
The most popular elastic impression materials in modern prosthetics are A-silicones. The main advantages of A-silicones are low shrinkage, hydrophilicity, high definition of the impression, easy removal of the impression from the oral cavity, and shape retention for a certain period of time.